Energy-to-Coins: miners providing computer power to solve cryptographic puzzles
Back in the 2010s, miners of Bitcoin were the pioneers of the new financial world. Now cryptocurrency mining is a business with its associated costs and projected profits. Let’s see if Bitcoin mining is profitable now or if more profitable alternatives have emerged.
Old-school mining
Bitcoin mining rewards halve about every four years. Bitcoin was first mined in 2009, back then, mining one block would get you 50 BTC. In 2012, that amount was halved to 25 BTC. By 2016, that figure was halved again to 12.5 BTC. On May 11, 2020, the reward was halved again to 6.25 BTC. Sometime in 2024, the reward will halve again to 3.125 BTC. On October 18, 2023, the price of Bitcoin was around $28,400, which meant you could get about $177,500 for a single block.
Does it seem simpler than simple?
To be able to mine, you need to invest in one of the best graphics processors (GPUs, often called graphics cards) for your computer or an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC). Performance GPUs can range in price from $1,000 to $2,000; ASICs can cost much more, up to tens of thousands of dollars.
Today, most of the hash power of the Bitcoin mining network consists almost entirely of ASIC mining farms and aggregations of individual miners. Today’s ASICs are many orders of magnitude more powerful than CPUs and GPUs, and are increasing in processing power and energy efficiency every year as new chips are developed and introduced.
What miners do with their mining rigs is guess a number that is smaller than the target hash. The target hash is a hexadecimal number greater than the number of hashes to be solved. The miner who first finds the solution to the puzzle receives a mining reward, and the probability that a participant finds the solution is equal to a fraction of the total mining power on the network.
Participants with a small percentage of mining power have a minimal chance of discovering the next block on their own. For example, a graphic processor you can buy for a couple of hundred dollars will represent less than 0.001% of the network’s mining power. With such a small chance of finding the next block, it may take a long time – if ever – before you solve the hash, because it all depends on how many hashes per second your machine can generate. You may never recoup your investment.
More downsides to bitcoin mining…
The risks of mining are often financial and legal in nature. As mentioned above, Bitcoin mining and mining, in general, is a financial risk, as you can put a huge amount of effort into buying hundreds or thousands of dollars worth of mining equipment but not get a return on your investment.
If you are thinking about mining and you live in a country where it is illegal, you should reconsider your decision. Researching your country’s laws and general attitudes towards cryptocurrency may also be a good idea before investing in mining equipment.
Another potential risk associated with the rise of Bitcoin (and other Proof-of-Work Algorithms) mining is the power consumption required by the computer systems that run the mining algorithms. While the efficiency of ASIC chips has increased dramatically, the growth of the network itself has outpaced technological advances. As a result, there are concerns about the environmental impact and carbon footprint of bitcoin mining. Mining equipment also generates a lot of heat, so your cooling bill is likely to increase, especially if you have one or more ASICs running 24 hours a day.
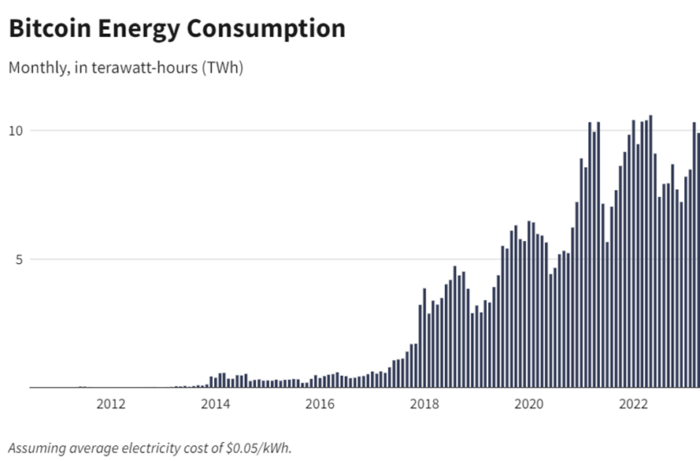
Bitcoin currently consumes about 150 terawatt hours of electricity annually – more than the entire country of Argentina with a population of 45 million people. The production of this energy releases about 65 megatons of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere each year, which is comparable to Greece’s emissions, making cryptocurrency an important contributor to global air pollution and climate change.
In addition to being very resource-intensive mining can put a lot of strain on your GPU or other mining equipment. In fact, it is not uncommon for GPUs to wear out or for mining rigs to catch fire.
Conclusion
Bitcoin and its mining is the first step in the world of digital finance. And first steps, as we all know, are not always perfect. It’s time to rethink the “traditional” approaches to cryptocurrency mining. Whether there are more profitable alternatives to Bitcoin and its mining – let’s consider in the next article.
THIS IS DIVA.EXCHANGE
The non-profit association diva.exchange, Switzerland, uses a barrier-free and collaborative approach to create free banking technology for everyone. Open-source technology ensures the privacy of all participants in the financial system of the future. The blockchain-based system is fully distributed. Everyone can participate in diva.exchange.
Diva.exchange is committed to the belief that only commercially free technology can reliably protect user privacy.
Collaboration with the scientific community plays an important role in the development of diva.exchange. The results of diva.exchange research are constantly being validated by academic institutions and publicly presented at specialized conferences.
LEARN MORE ABOUT OUR WORK
All technical information is available at: https://github.com/diva-exchange/
I2P beginner’s guide and installation guide:https://www.diva.exchange/en/privacy/introduction-to-i2p-your-own-internet-secure-private-and-free/
All videos are here: https://odysee.com/@diva.exchange:d/
Introduction to I2P: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/I2P
Testnet of diva.exchange: https://testnet.diva.exchange
CONTACT US
Twitter: https://twitter.com/@DigitalValueX
Mastodon: https://social.diva.exchange/@social
If you still have questions you can always find us on Telegram: https://t.me/diva_exchange_chat_de (in English, German, or Russian)
